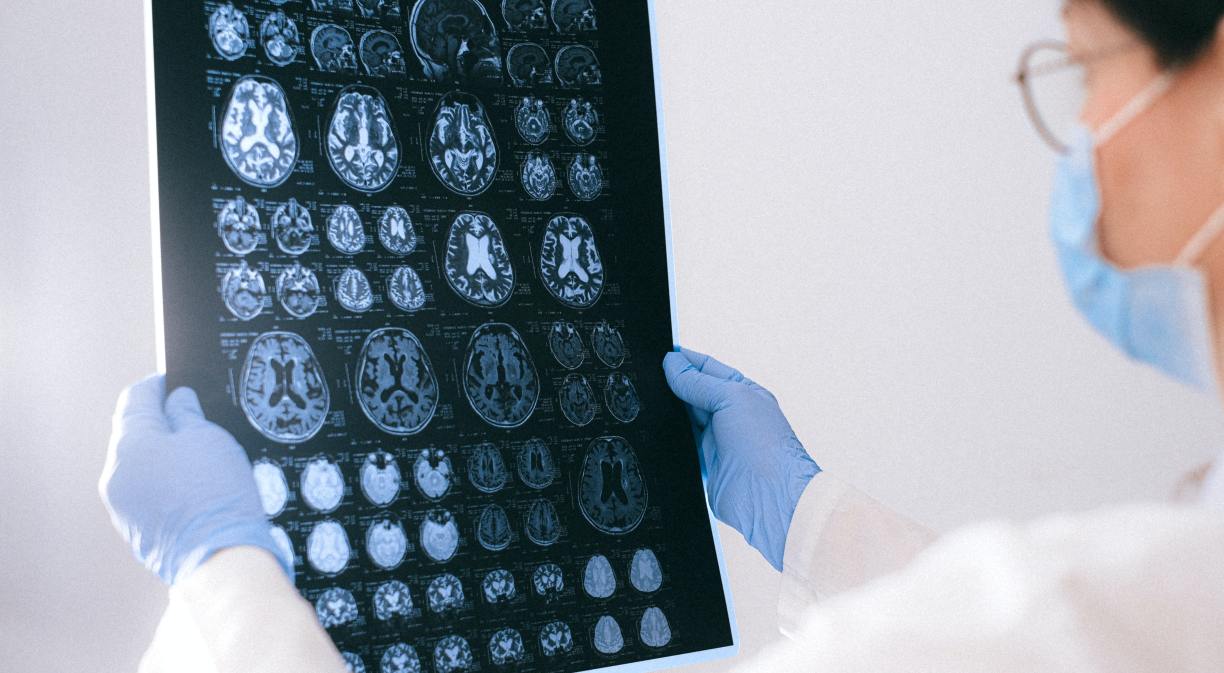
The causes of Alzheimer’s, a disease that currently affects around 800,000 people in Spain, are still unknown. However, Artificial Intelligence can provide early detection and be used as a tool to aid its prevention and monitoring.
This disease not only causes memory loss, but also other kinds of cognitive impairments that affect conduct and behaviour. As the Pasqual Maragall Foundation indicates, this progressive deterioration manifests itself in language alterations, difficulties in planning tasks and problem-solving, time-related, spatial and personal disorientation and other effects such as anxiety, apathy, sadness, sleeping disorders and disconcerting attitudes.
Alzheimer’s is the leading cause of dementia around the world. We should bear in mind that in 2015, according to data collected by the SEN (Spanish Society of Neurology), it affected around 47 million people, and this figure is estimated to rise to 130 million by 2050.
It’s also the disease that generates the greatest degree of disability among the elderly in Spain. This makes it a public health priority and a social and healthcare problem that affects not only the sick but also their families, who ultimately become their carers on many occasions. The lack of independence and progressive limitation of autonomy also generates economic and social costs.
Practical applications in the detection
While the mechanisms behind the disease are still being discovered, researchers have learnt that the initial lesions in the brain may begin up to 20 years before the first symptoms actually appear.
According to the SEN’s data, around 40,000 new cases of Alzheimer’s disease are diagnosed in Spain every year. However, they estimate that 80% of mild cases of Alzheimer’s are still undiagnosed and that 30%-40% of all cases are undiagnosed. This is why early detection is so important.
The lack of data that could indicate the development of the disease in its very early stages is delaying the incipient application of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments to slow down cognitive deterioration and control behavioural disorders, as there are drugs that can maintain the patient’s neuro-psychological and functional state for a degree of time, according to the neurologists.
In response to these needs, artificial intelligence (AI) has become an important tool in the field of health and its practical applications are focusing on the area of diagnostics in particular.
Artificial intelligence, key to diagnosis
In the field of neurology, it’s chiefly applied to assist image processing and improve studies based on tests such as PET and magnetic resonance. The reason is that this technology helps to differentiate between healthy and diseased brain images and can also perform a segmentation of the tumour’s tissue and a classification of the patient’s different disorders.
The potential of AI in this area has led many technology companies to seek to work on the creation and development of new tools. After creating an artificial intelligence neuro-imaging platform, medical technology companies such as QYNAPSE have launched the QyScore platform to offer automated quantification of a wide range of neuro-degenerative and neuro-inflammatory markers, with the incorporation of advanced visualisation capabilities accessible for doctors.
The platform, which has already been authorised by the FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration), helps specialists to make early diagnoses and monitor patients suffering from Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders, as they have access to a set of regulatory data obtained by means of the automated comparison of the patients’ results with a broad database of other healthy patients, who act as a control group.
A map of the brain
The research and innovation must also be based on cooperation and the dissemination of new knowledge. Because the brain remains an organ about which there is still much to be discovered. However, a neuro-imaging company based in Barcelona was recently able to develop a map of the brain by means of Artificial Intelligence and software engineering.
The system, designed by QMENTA, can quantify and share images of the brain anywhere and at any time, as it’s hosted in the cloud. Doctors can thus make the best decisions, providing a boost for research and enabling the experts to find a cure for diseases that don’t yet have one.
This company has succeeded in creating neuro AI tools that can provide an insight into the brain’s anatomy by accentuating the tissues’ changes or damage and hyper-intensities in colour and 3D.
They’ve also created maps of the brain’s network to view the changes in the connections due to diseases or lesions. These state-of-the-art algorithms, powered by Machine Learning, can help to automate the work of the researchers and medical specialists, optimising the time and resources available to them and promoting the sharing of new knowledge.
Tools based on the new technologies are now bringing the medical community closer to finding cures and treatments that can prevent the development of diseases such as Alzheimer’s.