Before analysing what the IIoT or Industrial Internet of Things is, let’s briefly define the IoT.
What is the IoT?
The IoT or Internet of Things refers to the set of devices or objects with the capacity to connect and exchange data with each other through a mobile network.
Some of its main uses are to streamline, improve and automate processes related to mobility, the management of public spaces, the agri-food sector and industry. The IIoT is precisely related to the industrial field.
What is the IIoT?
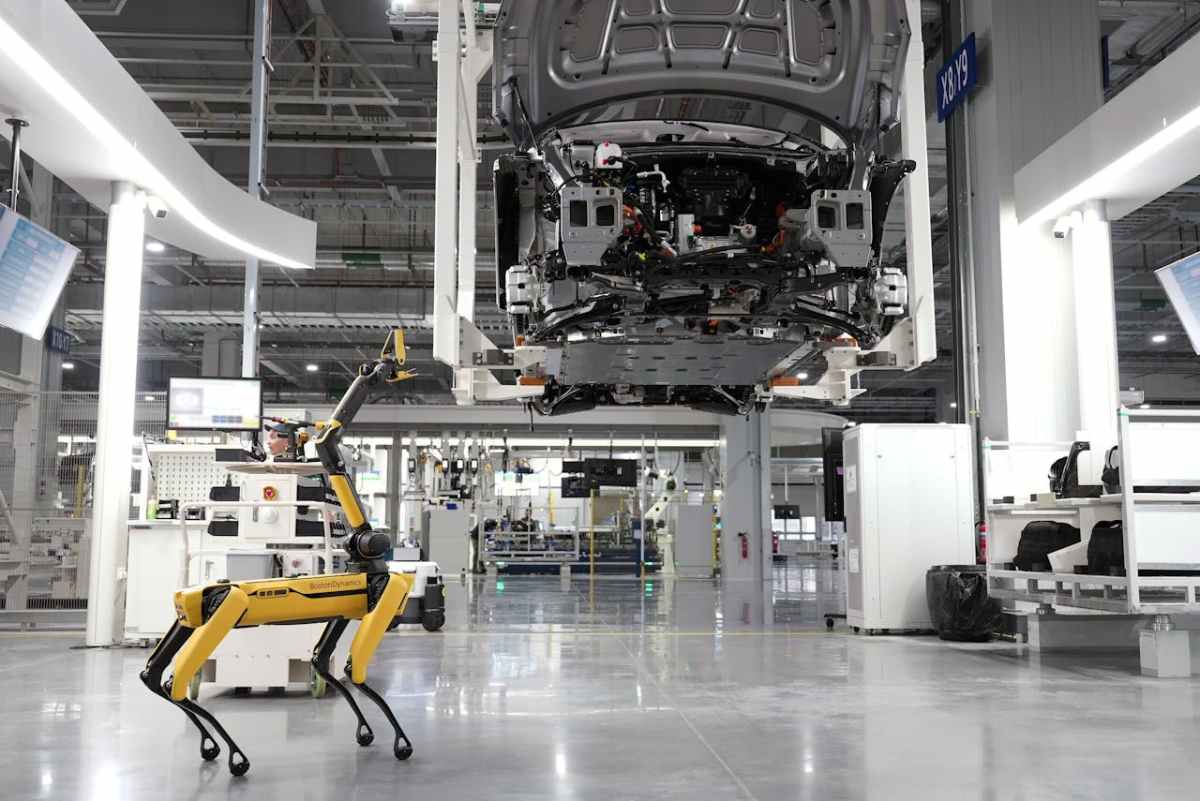
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is defined as the subset of the IoT focused on industrial applications through the interconnection of sensors, devices or intelligent machines that collect, analyse and share data in real time to optimise processes and make decisions in industrial environments.
The IIoT is considered a key component of Industry 4.0, a concept that refers to the integration of advanced technologies to transform industrial management towards greater levels of interconnectivity and digitalisation.
Benefits of the Industrial IoT
The Telefónica Tech blog highlights a number of advantages of the Internet of Things Industrial (in Spanish). Let’s see what they are:
- Visibility. Having greater visibility in processes thanks to IIoT technology makes it possible to anticipate operational anomalies by identifying faults that may occur at any point in production. This means that any adjustments that may be necessary can be made quickly.
- Greater productivity. The use of Industrial IoT tools means that workflows can be executed at a faster pace without compromising product quality, which also means greater productivity.
- Faster improvement cycles. Having real-time data collection and analysis helps to speed up the search for possible solutions to unexpected situations that may have arisen.
- Preventive maintenance. The possibility of anticipating hypothetical errors is another of the benefits of the IIoT, since intelligent sensors transmit data that anticipates the need for possible part changes or some kind of maintenance before the failure becomes more serious.
- Increased quality. If there is any kind of destabilisation in issues of great relevance to production, there may also be alerts that help to get the process back on track.
- Optimised supply chain. Inventory can be tracked throughout the supply chain using tags or sensors, providing precise information on issues such as manufacturing cycle times, the status of goods or anticipating unforeseen damage.
Differences between IoT and IIoT
The difference between the Internet of Things and its industrial variant lies in the fact that the latter must have a level of precision, reliability and security that can be critical.
The first difference lies in the approach taken: while IoT is aimed at individuals or consumers in the home to make everyday life easier, IIoT is aimed – as its name suggests – at industrial environments.
Another difference is in robustness and scalability: the IoT tends to be less demanding and simpler, while the Industrial Internet of Things has to be more robust and scalable in order to operate in the harsh conditions often found in industrial production.
In terms of security, and without underestimating its importance in the IoT, in its industrial aspect it is even more relevant. The possible implications and consequences of cybersecurity breaches in industry can be of a much greater magnitude.