- Depending on the means of transmission, telecommunications can be wired or wireless.
- Depending on the service offered, telecommunications can be voice, data, radio or video.
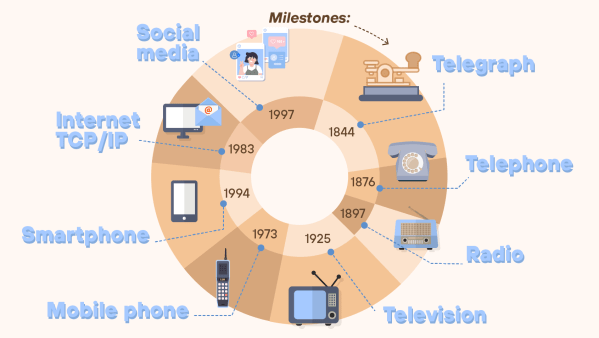
Telecommunications are the set of systems and technologies that enable both the transmission and reception of information, whether images, data or videos, with different types existing depending on various criteria, such as the medium by which it is transmitted or the service offered.
These types have evolved alongside the history of telecommunications.
By means of transmission
Depending on the means of transmission, there are two different types: wired and wireless telecommunications.
Wired telecommunications
In this case, information is transmitted through a physical medium (specifically, a cable) through which the signal is transferred between two points.
Fibre optics, Ethernet and coaxial cable are some examples of this type of wired telecommunications.
Some of the main characteristics of this type of telecommunications, depending on the medium, are speed (faster than wireless), stability (more robust and therefore less likely to receive external interference) and security.
Wireless telecommunications
Unlike the previous case, communication takes place without the existence of physical supports such as cables and is carried out by means of electromagnetic waves.
The main features of this type of telecommunications are the possibility of simultaneous communication from multiple devices and the ability to have mobility without the physical ‘tie’ of a cable, which also implies a greater degree of convenience.
In this type of telecommunications, signals (such as data or voice) are digitised and then encoded into a radio frequency signal, which is then amplified and transmitted through the air via antennas. Later, a receiver picks up that signal, decodes it and converts it back into the original information.
By service
Depending on the service, they can be classified into voice and data on the one hand and broadcasting and video on the other.
Voice services
This category includes fixed telephony, one of the icons of telecommunications, whose history dates back to the 19th century.
Despite its declining importance in telecommunications as a whole, fixed telephony is still used in business and emergency settings.
In addition to traditional fixed telephony, voice over IP (VoIP) allows voice calls to be made over the Internet rather than the traditional telephone network.
Mobile telephony also falls under voice services, although it is true that it also includes many other services that we will analyse later.
Data services
Data networks, of which the Internet is the prime example, are defined as systems of interconnected devices (including servers, computers and telephones).
These networks work by breaking down information into data packets that travel across the network, with each packet containing information about its origin and destination.
As mentioned above, the Internet is a giant global network of networks that allows one device to communicate with another regardless of the distance between them.
It uses TCP/IP protocols, the inclusion of which led to it being known as the Internet after previously being called Arpanet, this network being the origin of the Internet.
We could summarise by saying that the Internet is the largest and most complex example of data networks, and it is precisely this technology that allows the Internet to function.
Video and broadcasting services
Not as old as the use of landline telephony, but both technologies now being over a century old, both radio and television are examples of the types of telecommunications that offer video or broadcasting services. This mass broadcasting to large audiences is characterised by its unidirectionality, unlike other types of telecommunications, which are marked by bidirectionality due to the